Our Radiology department is fully digital, from diagnostic rooms to portable x-ray units. Digital radiography (DR), as compared to its predecessor, produces far sharper images, since digital sensors aid in creating higher resolution images. This aids our doctors to see even the smallest detail that would easily be missed.
One of the main advantages of DR is that the amount of radiation required to produce a digital image is significantly less than conventional film or Computed Radiography (CR). Reduced radiation exposure is beneficial to patients and employees alike. Having DR allows us to continue our commitment to our patients in reducing radiation exposure and adhering to radiation safety practices.
Anderson Diagnostic Imaging Department is accredited by the American College of Radiology (ACR) in Breast MRI, Breast Ultrasound, CT, Mammography, MRI, PET and Stereotactic Breast Biopsy. ACR Accreditation is recognized as the gold standard in medical imaging and demonstrates to our patients that we are committed to providing the safest and best quality care possible.

Computed Tomography (CT) is a diagnostic exam that uses special X-ray equipment to capture extremely clear images of your bones, muscles, body tissue, organs and blood vessels. These images help doctors diagnose and treat problems as accurately and swiftly as possible.
CT offers more detail than a standard X-ray because it provides cross-sectional images, often called “slices,” of your body. During your CT exam, an X-ray beam moves completely around you, gathering information from hundreds of different angles. A computer then takes these images and assembles a three-dimensional picture of the area being studied.
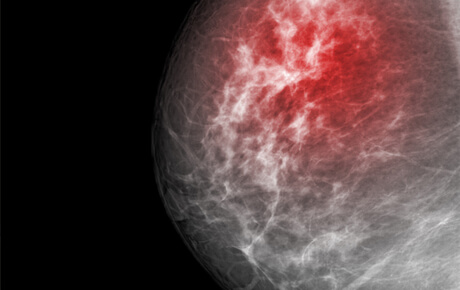

Offering the area’s only 3D Mammogram for better, earlier detection.
A mammogram is an X-ray image of your breast used to screen for breast cancer. Mammograms play a key role in early breast cancer detection and help decrease breast cancer deaths.
During a mammogram, your breasts are compressed between two firm surfaces to spread out the breast tissue. Then an X-ray captures black-and-white images of your breasts that are displayed on a computer screen and examined by a doctor who looks for signs of cancer.
A mammogram can be used either for screening or for diagnostic purposes. How often you should have a mammogram depends on your age and your risk of breast cancer.
Learn more about Anderson Regional Breast Center.

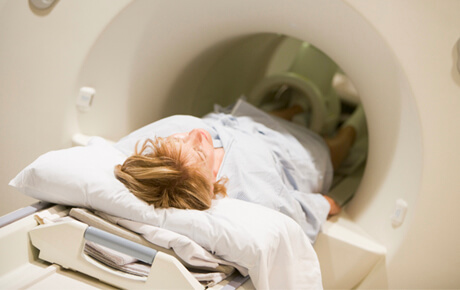
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging exam that uses a powerful magnet and radio waves to create detailed images of your internal anatomy. These images help doctors learn how your body is functioning and pinpoint problems.
Anderson is proud to offer the area’s only Open MRI.
Though any MRI is painless, an open MRI can be unpleasant for patients who are claustrophobic and for people who are physically too large to be in a closed MRI tunnel. A benefit of the open MRI is that the patient is able to see the room surroundings from inside the magnet; this minimizes claustrophobia. During brief intervals between scans, the patient is able to move around more freely than a traditional closed bore magnet. This also minimizes claustrophobia.
Our Phillips Ingenia 1.5T wide bore magnet boasts a 70 cm (27.5 inches across) opening that helps relax patients and reduce anxiety. It offers exceptional MR imaging for detection and characterization of tumors, and staging and therapy monitoring in breast and prostate cancer patients.
Anderson Regional MRI Center is conveniently located between Anderson- North and Anderson- South at 2115 13th Street, Meridian, MS 39301. For more information, please call 601.703.5720.
Positron Emission Tomography/Computed tomography (PET/CT) is a diagnostic imaging tool that combines the two scan techniques that form its name. PET/CT uses a small dose radiation to create detailed images of structures and function inside your body and can detect problems that don’t show up on other types of diagnostic imaging exams.
During a PET/CT scan, you are first injected with a radioactive substance. Lying on a flat table, you move slowly through a donut-shaped machine that detects positrons — the tiny particles given off by the radioactive material, which was injected prior to the test. The machine takes a series of images, which are then assembled to create a three-dimensional image of your body.
A radiologist interprets the results of your exam and reports them to your physician.
Nuclear medicine uses tiny amounts of radioactive substances to help doctors diagnose and treat a variety of health problems and diseases. It provides information about the structure and function of your body that can’t be found using other imaging exams.
When you have a nuclear medicine exam, you’ll be given a small dose of radioactive material. This radioactive “tracer” moves to the organ to be studied where it gives off energy as gamma rays. A gamma camera detects these rays and, with the help of a computer, produces images and measurements of organs and tissues.
From watching a baby in the womb to detecting heart problems, Anderson brings you the latest advances in ultrasound to meet a wide range of imaging needs. Ultrasound (also called sonogram) is a quick and easy diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the organs and systems within the body. These sound waves reflect off of body structures and are then analyzed by a computer to create a two-dimensional picture. Your exam will be performed by registered sonographers, including board-certified radiologists.
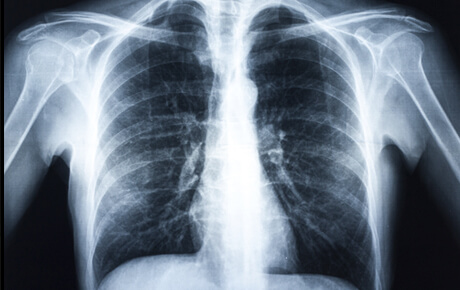

While the field of imaging has grown dramatically over the years, X-rays are still the most common type of radiology exam. X-rays use external radiation to make clear pictures of bones, organs and other areas inside your body to help doctors diagnose and monitor health conditions.
©2024 Copyright | Website Privacy Policy | Digital Marketing by Authority Solutions®