Did you know heart attacks have beginnings? These "beginnings" occur in over 50% of patients. Most importantly, if recognized in time, these "beginnings" can be treated before the heart is damaged!
If you have had a heart attack, the following tests and procedures may be performed:
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
This test to shows the electrical conduction of the heart will be one of the first used to diagnose a heart attack. During a heart attack, the heart muscle is injured and it won't conduct electricity normally. This will be shown on the ECG. Initial blood tests may be done to determine if there has been damage to your heart. If damage to the heart muscle has occurred, enzymes slowly leak into your blood flow. These enzymes are measured in blood tests called troponin and CK total.
Cardiac Nuclear Scan
This test helps identify blood-flow problems with the heart. By injecting radioactive material through an IV site, physicians will be able to identify areas of the heart that are not allowing blood to flow properly.
Echocardiogram
This test can help identify whether an area of your heart has been damaged by a heart attack. Using sound wave technology, it can provide images of your heart and can detect poor heart wall motion, an indicator of heart damage.
Cardiac Catheterization
This test can help determine whether your coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked. This is done by placing a small catheter into an artery, usually in the groin or wrist, which is fed to the arteries of the heart. A liquid dye is then injected to visualize the coronary arteries, thereby revealing areas of blockages (also known as angiography). Additionally, if a blockage is discovered, the area can be treated while the catheter is in place in a procedure called angioplasty.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Similar to the cardiac catheterization, this test can actually treat blockage by using balloon angioplasty and/or by placing a stent. Balloon angioplasty is a catheter with a balloon tip that is fed through the arteries to the blockage. The balloon is opened and pushes plaque back against the arterial wall, which allows for improved blood flow. Coronary stenting often accompanies angioplasty. Stents are small wire mesh devices used as scaffolding to support and open the arterial wall, thereby reducing the chance the artery will re-close. PCI usually takes 1-2 hours to complete the entire procedure and is performed with local anesthesia and procedural sedation and analgesia. Blood thinners may be used through an IV to prevent clotting. An anti-platelet medication along with aspirin is usually prescribed for a minimum of three months up to 12 months (depending on physician practice) to prevent blood clot formation within the affected vessel.
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
Of those people who have heart disease, approximately 10 percent will undergo coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). Those with severe narrowing or blockages, especially involving multiple arteries, may be considered for bypass surgery. This is an operation performed by a surgeon and done under general anesthesia. The surgeon takes a healthy vessel from the leg, chest or arm and creates a bypass around the blockage, restoring blood flow to the heart muscle. Typically, one to five bypasses can be done, depending upon how many coronary arteries are blocked. A CABG procedure usually requires about a five-day stay in the hospital and up to three months to fully recover from the surgery.
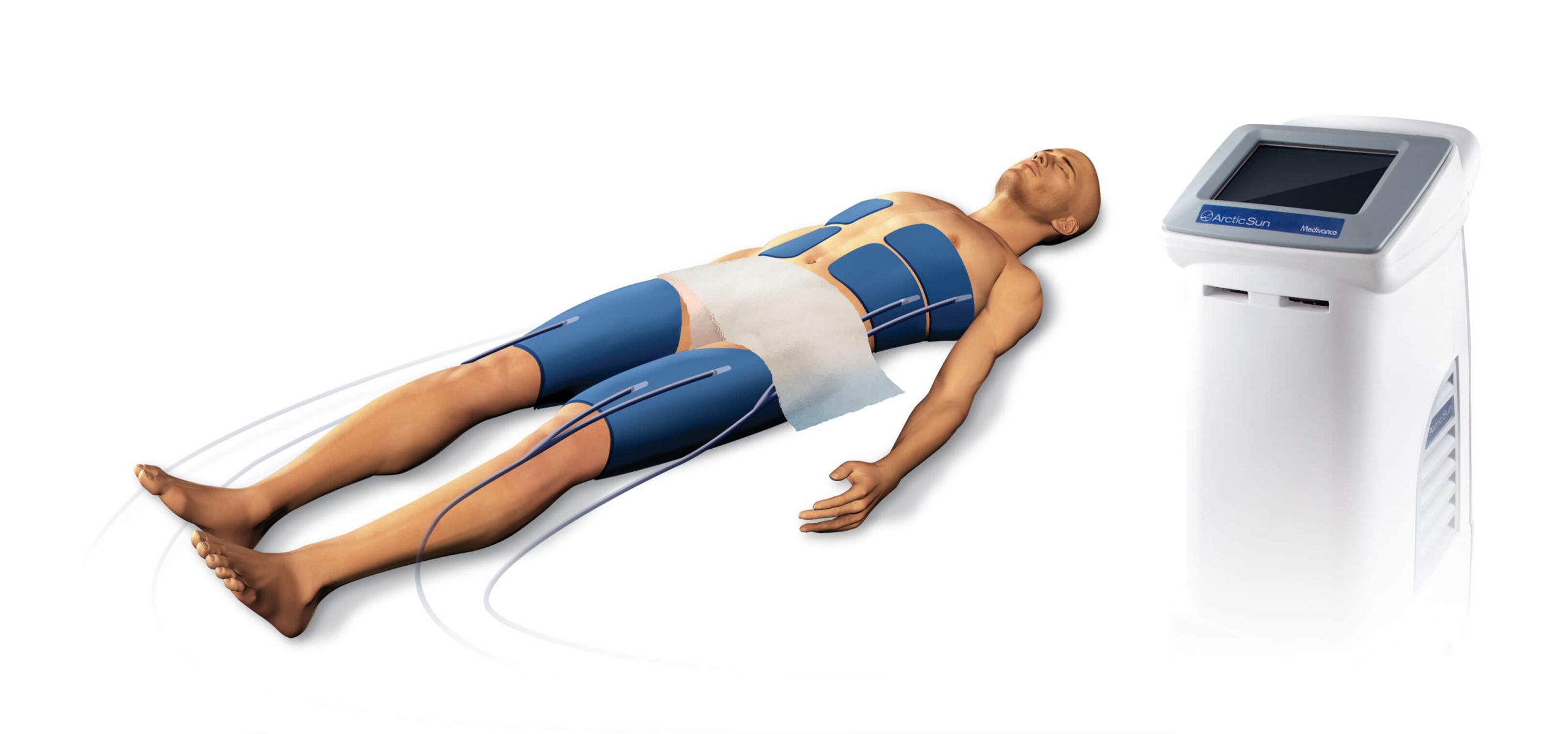

Anderson Regional Medical Center offers Meridian’s only Arctic Sun 5000, a highly advanced temperature management therapy for cardiac arrest patients.
Body temperature, a measured and controlled vital sign, can impact a patient’s recovery from cardiac arrest and can be intentionally manipulated as a treatment option. Therapeutic hypothermia is a process in which the patient’s body temperature is cooled for 24 hours and then slowly re-warmed to prevent irreversible neurological damage.
This technology is used on complete cardiac arrest patients in the Emergency Department, and it can also can be used on patients in the Cardiac Catheterization Lab, Intensive Care Unit, Cardiac Care Unit and other units.
The American Heart Association cites cooling as a standard of care following cardiac arrest. Unlike traditional cooling methods, such as ice or water blankets, the Arctic Sun incorporates advanced, non-invasive technology to adjust body temperature to exacting specifications. This results in more efficient temperature management and can minimize damage to the heart and brain. The precise, slow re-warming provided by the system is also beneficial for recovery.
Hailed as a medical breakthrough by The Wall Street Journal’s Technology Innovation Awards, the Arctic Sun therapeutic temperature management device is the only precise, non-invasive patient cooling device used at more than 70 percent of the nation’s top hospitals.
©2024 Copyright | Website Privacy Policy | Digital Marketing by Authority Solutions®