Anderson Staff Takes CPR Training to the Next Level
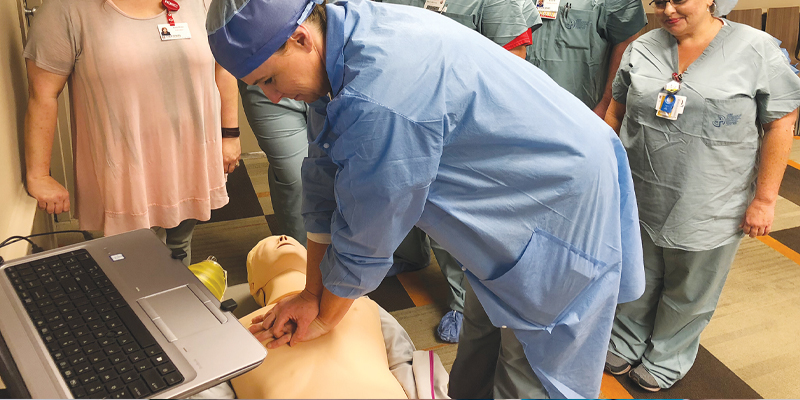

Anderson Regional Medical Center (ARMC) is the first acute care hospital in Mississippi to take CPR training to the next level by implementing the American Heart Association’s Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI®) program.
“RQI is a new and truly innovative program that has transformed the way hospitals view CPR competency for their staff,” said Lisa Primiani, Development Manager for the American Heart Association’s Resuscitation Quality Improvement program, Greater Southeast Affiliate. “Currently, hospital staff members are required to attend a CPR class once every two years. Our science has proved that CPR skills decay in as little as three months.”
Enter: RQI. Hospital staff members practice their CPR skills at the point of care (on a hospital floor), using real-time audio-visual feedback in 10-minute sessions every 90 days to achieve and maintain high-quality skills.
Kim Riley, ARMC Project Coordinator and AHA-Training Center Coordinator, said, “The RQI program makes CPR a regular practice for our clinical personnel. When using RQI, they feel more confident with their skills, and RQI Analytics prove that CPR quality is improved.”
“Currently CPR and respiratory skill testing takes place in an instructor-led arena. Testing every two years not only allows for degradation of skills, but you must also factor in the subjectivity involved in instructor evaluations. Embracing the use of the RQI system will give effective, consistent feedback to all learners, fostering competency and improving patient outcomes,” commented Melissa Mason, BSN, Critical Care Educator and AHA-Faculty/Instructor.
The RQI program has been developed through a unique collaboration between the Association and Laerdal Medical, wherein the Association provides expertise in evidence-based research and best-practice guidance, and Laerdal Medical provides proven simulation/learning technology.
Utilizing a variety of learning tools with an emphasis on skills mastery through low-dose, high-frequency sessions and performance feedback, the RQI program offers three components: cognitive, psychomotor skills and simulated patient cases.
• Cognitive may involve interactive lectures, videos or web-based content and is targeted to specific provider groups within the hospital and in other healthcare settings.
• Psychomotor Skills sessions monitor and report CQI metrics and equipment used in the healthcare setting, utilizing performance measurements completed within the healthcare facility’s clinical units.
• Simulated Patient Cases require students to assess and treat a virtual patient care scenario and are integral to assessing a student’s ability to apply their RQI skills to a real patient case.
During the skills session/assessment, students are provided real-time, audio/visual feedback through a laptop, and student performance data is archived in a learning management system (e.g. compressions of adequate rate and depth, full chest recoil, minimal interruption to compressions, avoidance of excessive ventilation). This data is used to track and document individual student performance.
“RQI is the gold-standard for resuscitation quality improvement and skills maintenance within hospitals,” said Primiani. “There is no other program for medical professionals that addresses skills decay and provides objective feedback. Hospitals credit RQI as a catalyst for a Culture of Resuscitation Excellence in their organization. Above all else, RQI is a clinical quality improvement program that saves lives.”
###
About Anderson Regional Health System
As the most comprehensive health system in East Mississippi and West Alabama, Anderson Regional Health System is the established leader in offering premier medical services. With two hospitals, a cancer center, and a network of clinics, Anderson’s healthcare professionals are committed to the mission of providing a heritage of healing and improving life for the people they serve.
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is devoted to saving people from heart disease and stroke – the two leading causes of death in the world. We team with millions of volunteers to fund innovative research, fight for stronger public health policies, and provide lifesaving tools and information to prevent and treat these diseases. The Dallas-based association is the nation’s oldest and largest voluntary organization dedicated to fighting heart disease and stroke. To learn more or to get involved, call 1-800-AHA-USA1, visit heart.org or call any of our offices around the country. Follow us on Facebook and Twitter.